- operations can be done anywhere in the list
- Basic operations
- insertion
- deletion
- retrieval
- traversal
어디에서나 삽입, 삭제, 추출 등이 가능하기 위해서
- insertion: pPre
- deletion: pPre. pLoc
- retrieval: key
등 포인터를 추가한다.
1. int 데이터 저장하는 리스트
gll.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int LData;
typedef struct node {
struct NODE* next;
LData data;
}NODE;
typedef struct gllist {
NODE* head;
int count;
NODE* pos;
}GLLIST;
GLLIST* createList();
void _insert(GLLIST* pList, NODE* pPre, LData d);
int _search(GLLIST* pList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, LData d);
void addNodeList(GLLIST* pList, LData d);
void _delete(GLLIST* pList, NODE* pPre, NODE* pLoc);
void deleteNodeList(GLLIST* pList, LData d);
int traverseList(GLLIST* pList, int fromWhere, LData* pDataOut);
void t_printList(GLLIST* pList);
void destroyList(GLLIST* pList);
void printList(GLLIST* pList);
- pos: traverse()시에 현재 위치 저장하는 포인터
- _insert, _search, _delete는 pPre, pLoc 등의 포인터를 받아서 실질적으로 삭제하는 역할을 한다.
- addNodeList, deletNodeList 는 내부에서 search 함수를 이용해 위치를 찾고 insert, delete등을 불러 기능한다.
- traverseList 는 리스트에 있는 데이터를 추출해낼 수 있는 함수
- printList는 처음에 내가 그냥 만든 리스트 모든 데이터 프린트하는 함수이고, t_printList는 traverseList()를 이용해서 전체 리스트를 프린트 할 수 있는 함수이다.
gll.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "gll.h"
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
GLLIST* createList() {
GLLIST* pList = (GLLIST*)malloc(sizeof(GLLIST));
if (pList != NULL) {
pList->count = 0;
pList->head = NULL;
pList->pos = NULL;
printf("list created! \n");
return pList;
}
return;
}
void _insert(GLLIST* pList, NODE* pPre, LData d) {
NODE* newNode = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = d;
if (pPre == NULL) {
//insert before head node
newNode->next = pList->head; //여기가 문제였음
pList->head = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->next = pPre->next;
pPre->next = newNode;
}
pList->count++;
printf("item inserted! \n");
}
}
int _search(GLLIST* pList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, LData d) {
for (*ppPre = NULL, *ppLoc = pList->head; *ppLoc != NULL; *ppPre = *ppLoc, *ppLoc = (*ppLoc)->next) {
if ((*ppLoc)->data == d)
return TRUE;
else if ((*ppLoc)->data > d)
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
void addNodeList(GLLIST* pList, LData d) {
NODE* pPre = NULL;
NODE* pLoc = NULL;
int found = _search(pList, &pPre, &pLoc, d);
if (!found) {
_insert(pList, pPre, d);
}
printf("add node list success! \n");
}
void _delete(GLLIST* pList, NODE* pPre, NODE* pLoc) {
if (pPre == NULL) {
pList->head = pLoc->next;
}
else {
pPre->next = pLoc->next;
}
free(pLoc);
pList->count--;
}
void deleteNodeList(GLLIST* pList, LData d) {
NODE* pPre = NULL;
NODE* pLoc = NULL;
int found = _search(pList, &pPre, &pLoc, d);
if (found) {
_delete(pList, pPre, pLoc);
}
}
int traverseList(GLLIST * pList, int fromWhere, LData* pDataOut) {
if (fromWhere == 0 || pList->pos == NULL) {
pList->pos = pList->head;
}
else {
pList->pos = pList->pos->next;
}
if (pList->pos != NULL) {
*pDataOut = pList->pos->data;
return TRUE;
}
else {
*pDataOut = 0;
return FALSE;
}
}
void t_printList(GLLIST* pList) {
LData data = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < pList->count; i++) {
traverseList(pList, i, &data);
if (data != NULL) {
printf("data: %d \n", data);
}
}
}
void destroyList(GLLIST* pList) {
NODE* pDel = NULL;
NODE* pNext = NULL;
for (pDel = pList->head; pDel != NULL; pDel = pNext) {
pNext = pDel->next;
free(pDel);
}
free(pList);
printf("list successfully destroyed! \n");
}
void printList(GLLIST* pList) {
NODE* temp = pList->head;
for (int i = 0; i < pList->count && temp!=NULL; i++) {
printf("data: %d \n", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "gll.h"
int main(void) {
GLLIST* pList = createList();
_insert(pList, NULL, 1);
addNodeList(pList, 3);
addNodeList(pList, 2);
printList(pList);
t_printList(pList);
destroyList(pList);
return 0;
}
2. 좀더 Generic 한 code
data.h
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct myData {
int key;
int field;
}MYDATA;
MYDATA* createData(int k, int f);
int compareData(MYDATA* arg1, MYDATA* arg2);
int compareKey(MYDATA* arg1, int key);
사실 compareKey나 compareData나 비슷한 역할을 한다. 헤더 파일에 이 구조체 간 key를 비교할 수 있는 비교 함수를 정의한 것이다. gll.c의 여러 함수들을 짜면서 누더기처럼 붙이다보니 일단 저렇게 두 개나 만들어졌으나, 적절하게 compareKey(int key1, int key2) 로 정리해서 compare 기능을 하는 함수를 하나로 만들어도 될 것이다.
data.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include "data.h"
MYDATA* createData(int k, int fi) {
MYDATA* myData = (MYDATA*)malloc(sizeof(MYDATA));
myData->key = k;
myData->field = fi;
printf("data created; [k: %d, f: %d] \n", myData->key, myData->field);
return myData;
}
int compareData(MYDATA* arg1, MYDATA* arg2) {
int result = arg1->key - arg2->key;
return result;
}
int compareKey(MYDATA* arg1, int key) {
int result = arg1->key - key;
return result;
}
mylist.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include "data.h"
typedef struct node {
struct NODE* next;
MYDATA* dataptr;
}NODE;
typedef struct myList {
NODE* head;
int count;
NODE* pos; // for traverse
}LIST;
//ADT
LIST* createList();
int traverse_print(LIST* myList);
NODE* retrieveNode(LIST* myList, int key);
void destroyList(LIST* myList);
void addNode(LIST* myList, MYDATA* data);
void removeList(LIST* myList, int k);
//private functions
int _insert(LIST* myList, NODE* pPre, NODE* newNode);
int _search(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, MYDATA* myDataPtr);
int _searchByKey(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, int key);
void _delete(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppDel);
user friendly 할 수 있는 ADT 와 ADT 함수 내에서 private하게 작동하는 내부 함수들의 관계로 만들어보았다.
위에 data.c에 compare 함수가 두 개가 생긴 것처럼 add/delete할 위치를 찾는 search()함수가 두 개가 되었다. 처음에 수업 ppt를 참고하면서 _search()함수의 마지막 매개변수를 MYDATA* 형식으로 하였는데, removeList, retrieveNode 등을 key를 기준으로 함수를 만들다보니까 MYDATA*를 넘겨주는 게 아니라 key를 넘겨주는 함수가 더 유용했다. _search()를 아예 없애고 addNode함수를 고치려니 귀찮아서(...) 그냥 남기고 _searchByKey()를 그냥 하나 더 선언해서 removeList 와 retrieveNode에 사용했다.
searchByKey 하나만 정의해서 addNode 에도 충분히 사용할 수 있을 것이다.
mylist.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "mylist.h"
//ADT
LIST* createList() {
LIST* myList = (LIST*)malloc(sizeof(LIST));
myList->count = 0;
myList->head = NULL;
myList->pos = NULL;
printf("list created! \n \n");
return myList;
}
int traverse_print(LIST* myList) {
NODE* temp = myList->head;
printf("------------ list elements: ----------\n");
for (; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next) {
printf(" key: %d, field: %d \n", temp->dataptr->key, temp->dataptr->field);
}
}
NODE* retrieveNode(LIST* myList, int key) {
NODE* temp = myList->head;
for (; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next) {
if (compareKey(temp->dataptr, key) == 0) {
//found the node;
printf("found the right node! \n");
return temp;
}
}
//unable to find the right node
printf("unable to find the right element \n");
return;
}
void destroyList(LIST* myList) {
NODE* pLoc = myList->head;
NODE* temp = NULL;
while (pLoc != NULL) {
temp = pLoc;
pLoc = pLoc->next;
free(temp->dataptr);
free(temp);
}
free(myList);
printf("list destroyed! \n");
}
void addNode(LIST* myList, MYDATA* myData) {
printf("[addNode] data inside: [k: %d, f: %d] \n", myData->key, myData->field);
NODE* newNode = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
newNode->dataptr = myData;
newNode->next = NULL;
printf("[addNode] created node data: [k: %d, f: %d] \n", newNode->dataptr->key, newNode->dataptr->field);
NODE* pPre = NULL;
NODE* pLoc = NULL;
int result = _search(myList, &pPre, &pLoc, myData);
if (result) {
printf("[addNode] _search successful! \n");
_insert(myList, pPre, newNode);
printf("[addNode] _insert successful! \n");
}
}
void removeList(LIST* myList, int k) {
NODE* pPre = NULL;
NODE* pDel = NULL;
if(_searchByKey(myList, &pPre, &pDel, k)){
_delete(myList, &pPre, &pDel);
printf("[removeList] node successfully removed from the list \n");
}
else {
printf("[removeList] unable to remove node \n");
}
}
//private functions
int _insert(LIST* myList, NODE* pPre, NODE* newNode) {
printf("[_insert] node data: [k: %d, f: %d] \n", newNode->dataptr->key, newNode->dataptr->field);
if (pPre == NULL) {
printf("[_insert] put in head \n");
// put int head
if (myList->head == NULL) {
// list is empty
myList->head = newNode;
}
else { // list isn't empty but has to go after head node
newNode->next = myList->head; // myList->head->next가 아니지!
myList->head = newNode;
}
}
else {
// pPre has location
printf("[_insert] put after pPre \n");
newNode->next = pPre->next;
pPre->next = newNode;
}
myList->count++;
}
int _search(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, MYDATA* myDataPtr) {
printf("[_search] data inside; [k: %d, f: %d] \n", myDataPtr->key, myDataPtr->field);
/* returns 1: call _insert / returns 0: do not call _insert */
*ppPre = NULL;
*ppLoc = myList->head;
if (*ppLoc == NULL) {
//the list is empty
return 1; // put in head
}
else {
while (*ppLoc != NULL) {
int result = compareData((*ppLoc)->dataptr, myDataPtr);
if (result == 0) {
// data are the same; cannot put it
printf("[_search] unable to put in data \n");
return 0;
}
else if (result < 0) {
// pLoc->data->key > myDataPtr->key => needs to go before current node
// go to next step
*ppPre = *ppLoc;
*ppLoc = (*ppLoc)->next;
}
else {
// pLoc->data->key < myDataPtr->key => put after pPre and before pLoc
// calls _insert(myList, pPre, myDataPtr)
break;
}
}
return 1;
}
}
int _searchByKey(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppLoc, int key) {
/* returns 0: unable to find the node that matched with the key
returns 1: found the right node with the key */
*ppPre = NULL;
*ppLoc = myList->head;
if (*ppLoc == NULL) {
//the list is empty
return 0; // put in head
}
else {
while (*ppLoc != NULL) {
int result = compareKey((*ppLoc)->dataptr, key);
if (result == 0) {
// found the right key
printf("[_searchByKey] found the right node with the key! \n");
return 1;
}
else if (result < 0) {
// go to next node
*ppPre = *ppLoc;
*ppLoc = (*ppLoc)->next;
}
else {
// pLoc->data->key < myDataPtr->key => unable to find the right key
printf("[_searchByKey] unable to find the node that has the key! \n");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
void _delete(LIST* myList, NODE** ppPre, NODE** ppDel) {
if (*ppPre == NULL) {
// node being deleted is the head node
myList->head = (*ppDel)->next;
}
else {
(*ppPre)->next = (*ppDel)->next;
}
free((*ppDel)->dataptr);
free(*ppDel);
}유난히 프린트 문이 많은 것은 포인터 때문에 헷갈려서 매개변수를 통해 값들을 잘 받아오고 있는지 확인하기 위해서 많이 찍어본 것이다. 대부분은 필요없는 출력들이다.
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mylist.h"
int main(void) {
LIST* myList = createList();
printf(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> DATA INSERTION <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< \n");
MYDATA* myData = createData(4, 7);
addNode(myList, myData);
printf("\n");
myData = createData(2, 9);
addNode(myList, myData);
printf("\n");
myData = createData(3, 19);
addNode(myList, myData);
printf("\n");
myData = createData(3, 29);
addNode(myList, myData);
printf("\n");
printf(">>>>>>>>>>>>>> SHOW INSERTION RESULT <<<<<<<<<<<<<<< \n");
traverse_print(myList);
printf("\n");
printf(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> TRY NODE RETRIEVAL <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< \n");
NODE* r_node = retrieveNode(myList, 2);
printf("retrieved data: [k: %d, f: %d]\n", r_node->dataptr->key, r_node->dataptr->field);
printf("\n");
printf(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> TRY NODE REMOVAL <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< \n");
removeList(myList, 2);
printf("\n");
traverse_print(myList);
return 0;
}
결과:
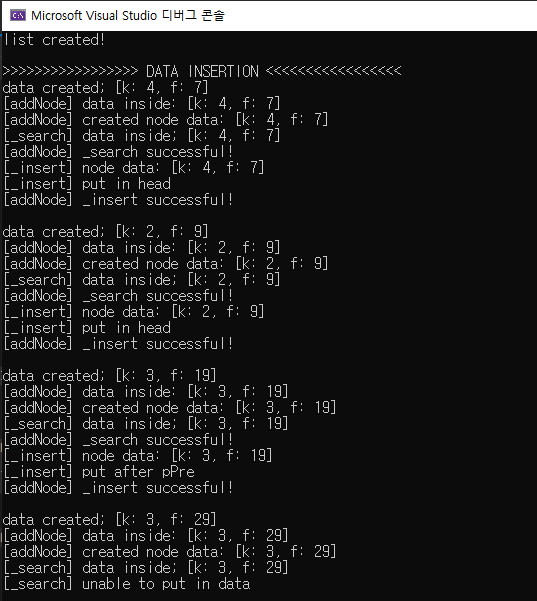
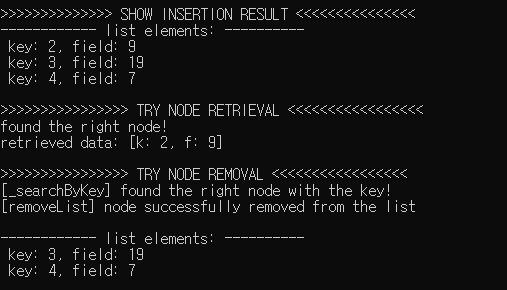
너무 누더기라 올리기도 부끄럽고 고칠 부분이 수두룩한 코드이지만... 일단 빠르게 넘기고 circular list, doubly linked list, tree 등을 시작해보려 한다. 포인터 때문에 단순 리스트 만드는 데 너무 오래 걸렸다... ㅜㅜ
'컴퓨터기본 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. Binary Search Tree (0) | 2021.06.14 |
|---|---|
| 5. Doubly Linked List (0) | 2021.06.14 |
| 3. Queue (0) | 2021.06.14 |
| 2. Stack (Linked list) (0) | 2021.06.14 |
| 1. 재귀, ADT (0) | 2021.06.14 |